Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA)
Types :
- Complete
- With Communication
- Corrected
1. Complete : has 2 circuits
- Oxygenated - Pulmonary circuit
- Un-Oxygenated - Systemic circuit
Therefore O2 therapy will not help as there is no path for O2 to reach systemic circuit.
Hence the child dies without t/t in 1st wk of life due to Hypoxia
T/t -
- PGE1 infusion to keep Ductus open (i.e to keep PDA)
- Emergency Surgery ( Create artificial ASD with balloon - Balloon atrial septostomy )
2. With Communication :
- With ASD - Small patent foramen ovale , Not helpful - hence cyanosis in 1st wk of life
- With VSD and PDA - good mixing of blood , therefore only mild cyanosis at 6-12 months of life.
3. Corrected : Physiologically behaves Normal.
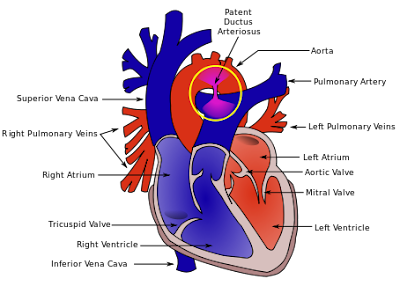
Ventriculo-Arterial disconcordance with Atrioventricular disconcordance (See the image below)
- Ventriculo-Arterial disconcordance means - Aorta arise from RV ; PA arise from LV
- AtrioVentricular dysconcordance means - Rt Arium opens into LV ; Lt Atrium opens into RV
 |
| Image Courtesy - DrAyushGoel |
MedicoNotebook - Founder : DrShiviMudgal , Co-Founder : DrAyushGoel




.png)



